In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and social responsibility, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) emerges as a potent force shaping business policies. In parallel, corporate governance, as a framework defining how companies are directed and controlled, also plays a pivotal role in steering businesses towards sustainable practices. Their interplay has profound implications for corporate decisions and actions, marking a significant shift in the global business landscape.
Corporate Governance: A Structured Approach
The system of rules known as corporate governance stands as the cornerstone of any company’s operation, providing a structured approach to direct and control a business. The principles and best practice provisions within this governance model allow for the balancing of a multitude of stakeholder interests, which may encompass shareholders, management, employees, customers, suppliers, creditors, and even government or community parties.
The set of rules that form the corporate governance system ensures long-term organisational success by facilitating fair, effective, and transparent decision-making processes. Additionally, corporate governance plays a crucial role in determining the distribution of rights and responsibilities among corporation participants. This system, both formal and informal, also stipulates the procedures and rules that govern corporate affairs decisions, reinforcing an organisation’s strategic focus on good governance and corporate accountability.
Impact of Good Governance in Practice
As a central component of a corporation’s framework, corporate governance’s importance cannot be understated. Its impacts are manifold, ranging from promoting corporate fairness, transparency, and accountability to risk mitigation and regulatory compliance.
A notable strength of good governance lies in its ability to facilitate a culture of responsibility. By promoting ethical and efficient practices, it strengthens stakeholder confidence—primarily that of investors—and fosters financial integrity. Additionally, good governance in practice aids in identifying and mitigating potential risks before their detrimental impact on the company, facilitating a risk-conscious decision-making environment.
Moreover, strong corporate governance serves to protect and enhance a company’s reputation. Through facilitating transparency and accountability, good governance can significantly improve investor and stakeholder perception, leading to increased investor confidence and potentially a higher market valuation. Lastly, it ensures corporations adhere to relevant laws, regulations, and ethical guidelines, thus avoiding scandals and potential legal issues.
Principles of Corporate Governance: A Guiding Force
Despite variations across different countries and companies, several key principles universally inform the practice of corporate governance. These principles focus on the rights and equitable treatment of shareholders, interests of other stakeholders, roles and responsibilities of the board, integrity and ethical behaviour, and disclosure and transparency.
A cornerstone of good governance is ensuring companies respect and uphold shareholder rights and interests, treating all equitably. Similarly, the interests of non-shareholder stakeholders, which can include employees, customers, suppliers, or the broader community, should also be recognized. The board of directors plays a vital role in guiding corporate strategy, monitoring management actions, and ensuring accountability to bolster this practice. Furthermore, maintaining ethical conduct is crucial in preserving public confidence and the integrity of markets. Finally, companies should ensure that their financial and operational performance is accurately disclosed in a timely and transparent manner.
The Board of Directors and Corporate Governance
The board of directors serves as the linchpin of corporate governance, overseeing and guiding management decisions to act in the best interests of shareholders and other stakeholders. The board’s role in facilitating the practice of good governance is reflected in its strategic formulation responsibilities, supervision of management, risk management, and corporate policies and compliance.
In its strategic role, the board oversees the company’s strategic direction and ensures the establishment of an effective strategic process. Furthermore, the board’s task is to supervise management performance, including the CEO, ensuring their actions align with the company’s strategy and shareholder interests. Risk management, another crucial area, sees the board identifying, understanding, and managing financial, operational, and reputational risks. Finally, the board’s responsibility extends to ensuring the company’s policies reflect its values and ethics and are adhered to, while also overseeing regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, corporate governance is an integral tool in enhancing corporations’ integrity and efficiency. In today’s corporate world, the impact of corporate governance principles and best practices provisions in facilitating transparency, accountability, and protection of shareholder rights is paramount. Effective governance thus builds a structure that benefits all involved by ensuring enterprises are governed in a manner that promotes prosperity and longevity.
The Implication of EU CSRD on Corporate Governance
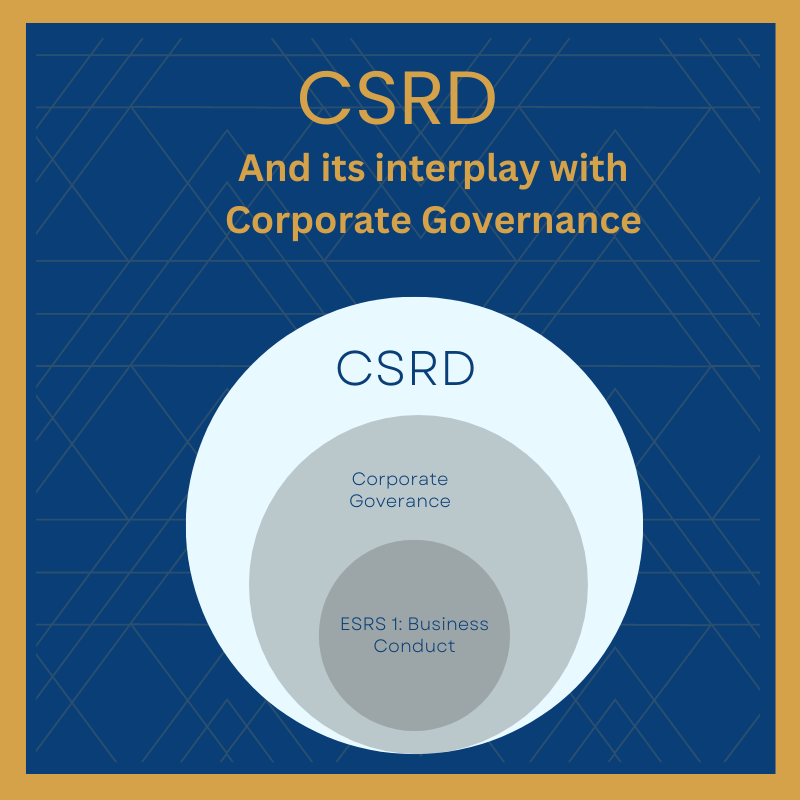
The CSRD, adopted by the European Union, mandates listed companies to report non-financial data, encompassing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) aspects. By integrating CSRD into their operations, corporations must adopt a new lens to scrutinize their governance structure. No longer can corporate governance be solely focused on financial performance and shareholder returns. It must encompass a wider range of stakeholders and consider the long-term sustainability of the business. It is a transformative force pushing corporate governance towards a more comprehensive, stakeholder-inclusive approach.
Corporate Governance: A Catalyst for Effective CSRD Implementation
In turn, robust corporate governance is crucial for the effective implementation of the CSRD. Without good governance structures and practices, companies may struggle to collect, verify, and report the required non-financial data accurately. Moreover, without an ethical leadership committed to sustainability, the CSRD may only result in superficial compliance, devoid of any real commitment to sustainable practices. Therefore, the quality of corporate governance can significantly impact the effectiveness of CSRD implementation.
To comply with the CSRD, companies must report on various matters as outlined in the standard ESRS G1: Business Conduct. This standard primarily focuses on specific business conduct matters as outlined by the CSRD. These include corporate culture, management of relationships with suppliers, anti-corruption and anti-bribery measures, political influence and lobbying, protection of whistleblowers, animal welfare, and payment practices, especially with regards to late payment to small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
For an in-depth understanding of corporate governance disclosure requirements, consider enrolling in our course, ESRS G1: Business Conduct.
Impact of the Interplay between CSRD and Corporate Governance
The interplay between CSRD and corporate governance not only affects individual companies but also the broader business ecosystem. It provides a regulatory platform to address global challenges such as climate change, social inequality, and corporate corruption. On the other hand, it poses new challenges for corporations, such as the need for system upgrades, skill development, and change management, to comply with the CSRD. Therefore, the interaction between CSRD and corporate governance can be seen as a disruptive yet progressive force, driving companies towards a more sustainable and socially responsible future.
Strategies for Harmonizing CSRD with Corporate Governance
So how can companies harmonize CSRD with their corporate governance? Firstly, board members and senior executives must champion sustainability, integrating it into their decision-making processes. Secondly, companies need to invest in training and systems to gather and report non-financial data accurately, following the requirements of the ESRS G1 standard. Finally, corporations should engage with stakeholders – employees, suppliers, customers, communities – to understand their expectations and include their perspectives in sustainability reporting.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable Future
The interplay between the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive and corporate governance signifies a step towards a sustainable future. It provides a tangible framework for businesses to act responsibly, meeting not only the economic expectations of shareholders but also the broader societal and environmental aspirations. As corporations navigate this dynamic landscape, the quality of their governance will prove critical in realizing the promise of the CSRD.
By understanding and leveraging this interplay, companies can position themselves as leaders in sustainability, setting the bar for corporate social responsibility and inspiring others in the process. As we continue to face global sustainability challenges, the collaboration of the CSRD and corporate governance will undoubtedly play an instrumental role in guiding our path forward.
Your Next Steps with CSRD and ESRS Sustainability Reporting
Get ready to lead the way towards a sustainable future with CSRD and ESRS Sustainability Reporting. Don’t wait any longer – it’s time to take action and position your company for success. Familiarize yourself and your team with the CSRD and ESRS reporting requirements today to ensure effective compliance and gain a strategic advantage in this evolving landscape.
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. We’ve got you covered with a wealth of resources available on The CSRD Compass website. Explore in-depth guides, explanatory articles, comprehensive courses, and expert analyses all in one convenient place. The CSRD Compass is your ultimate destination for everything related to CSRD and ESRS.
Together, let’s embark on this transformative sustainability reporting journey, future-proof your business, and make a positive impact on our world. Your first step starts here, with The CSRD Compass.


