In the complex world of corporate sustainability, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) has emerged as a central pillar. With an increasing number of stakeholders demanding accountability, this directive seeks to standardize and enhance the quality of sustainability reporting across Europe. This blog post seeks to simplify the complexities of CSRD compliance by making sense of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics that play a pivotal role in sustainable corporate reporting.
Understanding the CSRD
The CSRD builds on the foundations laid by the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD), seeking to amplify the transparency of corporate sustainability activities and practices. It requires companies to provide comprehensive, comparable, and reliable sustainability information that is crucial for stakeholders in decision-making processes.
One of the defining characteristics of CSRD is its widened scope. While the NFRD applied to large public-interest entities with more than 500 employees, CSRD extends this coverage to all large and listed companies, as well as public-interest entities, including SMEs and non-European companies. The primary objective is to create a consistent and comparable sustainability reporting framework across different sizes and types of organizations.
What is an ESG metric?
ESG metrics, a critical component of the ESG framework, offer a measurable standard that allows companies to evaluate their performance on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) aspects. These key ESG metrics facilitate companies in assessing their sustainability efforts, overall business performance, and the influence they exert on varied stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and even the nature being considered as a silent stakeholder.
In using ESG metrics, companies gain the ability to discern and mitigate ESG risks, amplify their ESG impact, and enhance their ESG reporting initiatives. Specific ESG indicators utilized may differ across sectors and companies, based on the relevance of certain ESG issues to their operations and stakeholders. Companies commonly employ quantitative ESG metrics to measure aspects like greenhouse gas emissions, energy usage, and waste production, while qualitative ESG metrics can track the company’s progress in areas such as diversity, business ethics, and corporate culture.
What types of topics do ESG metrics cover?
The scope of ESG metrics extends to a wide range of topics related to a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance. Examples of these include energy efficiency, carbon emissions, human rights, and aspects of diversity and inclusion. Moreover, specific ESG issues like sustainability, governance, business ethics, health and safety, and financial performance also come under the ESG metrics umbrella. With the growing importance of these metrics in assessing a company’s environmental and social impact, companies are ramping up their efforts to improve their ESG performance.
Why are ESG metrics so important?
In recent years, ESG metrics have gained immense importance as companies and investors aim to understand and quantify sustainability and social impact. These metrics provide a clear picture of a company’s ESG performance, enabling the identification of areas for improvement. ESG metrics play a crucial role in guiding businesses towards more informed decisions by identifying potential risks and opportunities. Furthermore, ESG metrics are now integrated into the decision-making processes of companies, facilitating the alignment of investments with sustainable practices.
How to track ESG KPIs / metrics?
Keeping a track of ESG Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) or ESG metrics is essential for enhancing an organization’s ESG performance. Organizations use ESG data, common ESG metrics, and KPIs to monitor their progress on ESG goals. Depending on the specific ESG challenges an organization faces and the interests of its stakeholders, the metrics chosen may vary. To effectively measure ESG performance, organizations must gather and analyze relevant data, establish suitable KPIs, and create a reporting framework that enables stakeholders to understand their ESG performance easily.
Why is ESG data management software important to manage ESG Metrics?
Finally, the importance of ESG data management software in managing ESG metrics cannot be overstated. This software enables companies to monitor their ESG performance, collect, analyze, and report ESG data transparently and consistently. Not only does it improve ESG performance and meet stakeholder expectations, but it also helps companies identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to address ESG issues. Therefore, ESG data management software is crucial for businesses to manage and report their ESG performance, helping them work towards sustainability while meeting stakeholder expectations. ESG data management software is becoming more important as companies must report various data points including data from their supply chain.
ESG Metrics in CSRD Reporting
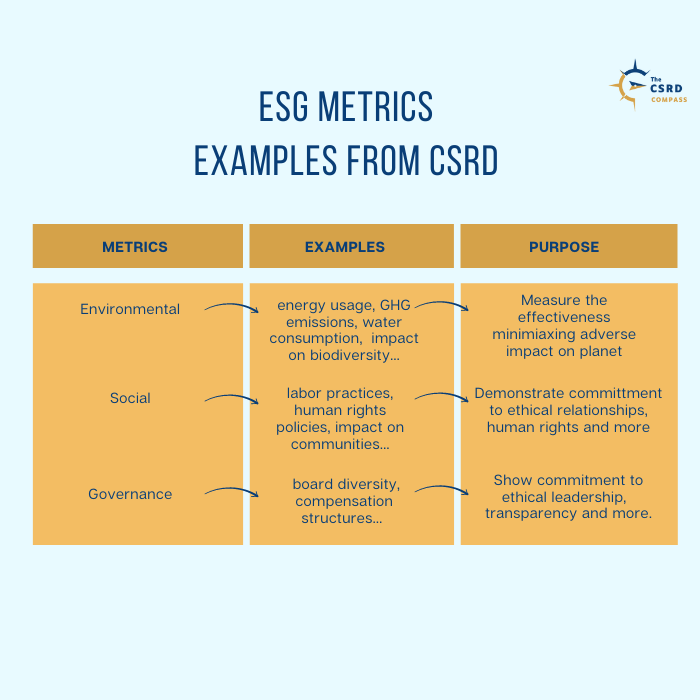
The incorporation of various ESG metrics into the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) marks a significant shift towards greater transparency and accountability in corporate practices and corporate sustainability reporting. ESG metrics serve as a comprehensive and structured methodology for organizations to articulate their performance in relation to environmental, social, and governance standards, offering stakeholders a clear view of their sustainability efforts and performance, including the progress they make over time.
Environmental Metrics in CSRD
Environmental metrics form a key part of this sustainability reporting process. These metrics encapsulate information about an organization’s environmental aspects, including energy usage, greenhouse gas emissions, waste production, water consumption, and impact on biodiversity and ecosystems. Such data portrays the extent of a company’s environmental footprint and reflects the efficacy of its initiatives to minimize adverse environmental impacts. In the era of CSRD, robust reporting on these environmental metrics has become increasingly important, as it demonstrates a company’s commitment to sustainable practices and their response to climate-related challenges.
Social Metrics in CSRD
Similarly, social metrics provide insights into an organization’s approach to managing relationships with various stakeholders including employees, workers in the value chain, suppliers, customers, consumers and end-users, and affected communities. These metrics may encompass details regarding labor practices, human rights policies, impact on local communities, customer satisfaction levels, and data protection measures. In the context of CSRD, social metrics serve to demonstrate a company’s commitment to maintaining ethical relationships, respecting human rights, and contributing positively to the communities it interacts with.
Governance Metrics in CSRD
On the governance front, metrics provide data on the organization’s leadership structure, corporate culture, efforts in anti-bribery and anti-corruption, as well as political influence and animal welfare if applicable. Key governance metrics often include board diversity, executive compensation structures, business ethics policies, and payment practices. These metrics are instrumental in illustrating a company’s commitment to ethical leadership, responsible management, and transparency in business practices.
Decoding ESG Metrics: The Imperative in the CSRD Era
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) has positioned ESG metrics as a pivotal element in corporate sustainability reporting. This shift necessitates companies to not only comprehend these metrics accurately but also interpret and report them proficiently. But the importance of ESG metrics goes beyond satisfying regulatory obligations; they are instrumental in guiding strategic decision-making and fostering sustainable business growth.
ESG Metrics for risks and opportunities management
ESG metrics provide valuable insights into an organization’s performance on environmental, social, and governance aspects. Interpreting these metrics can help organizations identify potential risks tied to their operations, such as environmental hazards, social grievances, and governance weaknesses. This allows companies to devise mitigation strategies, safeguarding their operations against potential disruptions and reputational damage.
On the flip side, these metrics can also reveal opportunities for businesses. For instance, a strong ESG performance might point to prospects for reducing operational costs through energy efficiency, enhancing customer loyalty through social initiatives, or attracting top-tier talent through a demonstrated commitment to ethical governance.
ESG Metrics and Stakeholder management
Beyond risk management and opportunity identification, ESG metrics can enhance a company’s reputation among its stakeholders. A robust ESG performance and transparent reporting can signal a company’s commitment to sustainability and ethical conduct. This can boost its appeal to consumers, investors, and employees alike, attracting investment, fostering customer loyalty, and promoting talent retention, thereby driving sustainable business growth.
Furthermore, comprehensive ESG reporting, as mandated by CSRD, can instigate productive dialogues between companies and their stakeholders. By sharing information about their ESG performance, companies can engage stakeholders in discussions about their sustainability goals, strategies, and progress. This can foster greater trust, improve stakeholder relations, and promote collaborative decision-making.
These dialogues can, in turn, lead to more robust relationships between companies and their stakeholders. Stakeholders who feel heard and involved are more likely to support the company’s initiatives, providing valuable feedback and even advocating on the company’s behalf. This strengthens the company’s social license to operate, enhances decision-making, and promotes corporate resilience.
To sum up
Overall, the ability to accurately decode ESG metrics has become a critical skill for businesses in the CSRD era. Effective ESG management and reporting can guide strategic decision-making, bolster reputation, attract investment, and drive sustainable growth. Moreover, it can foster stronger stakeholder relationships and catalyze better, more inclusive decision-making, ultimately leading to more resilient and successful businesses.
Check out our blog on the the Impact of ESRS on Stakeholder Trust and Engagement.
Conclusion: Preparing for the Future of Corporate Sustainability Reporting
The CSRD marks a significant step forward in corporate sustainability reporting, reflecting the growing importance of sustainability in the corporate world. Understanding and interpreting ESG metrics is a critical part of this journey.
Organizations that can decode these metrics, integrate them into their sustainability reports, and communicate their performance effectively will be better equipped to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the sustainability era. As the corporate world continues to evolve, mastering the art of interpreting ESG metrics under the CSRD will become increasingly important.
Remember, CSRD and ESG metrics are more than just buzzwords. They are instrumental in shaping sustainable corporate futures. The sooner you understand and integrate them into your business strategy and reporting, the better prepared you’ll be for a sustainable future.
Your Next Steps With CSRD and ESRS Sustainability Reporting
Get ready to lead the way towards a sustainable future with CSRD and ESRS Sustainability Reporting. Don’t wait any longer – it’s time to take action and position your company for success. Familiarize yourself and your team with the CSRD and ESRS reporting requirements today to ensure effective compliance and gain a strategic advantage in this evolving landscape.
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. We’ve got you covered with a wealth of resources available on The CSRD Compass website. Explore in-depth guides, explanatory articles, comprehensive courses, and expert analyses all in one convenient place. The CSRD Compass is your ultimate destination for everything related to CSRD and ESRS.
Together, let’s embark on this transformative sustainability reporting journey, future-proof your business, and make a positive impact on our world. Your first step starts here, with The CSRD Compass.


